
MoveIt connects a number of different fields and provides a lot of interfaces so that users can override different parts of the framework and implement new concepts without having to touching the core of the framework. The following lists the different types of plugins and provides an overview over the use of them within the framework.
Deprecated:
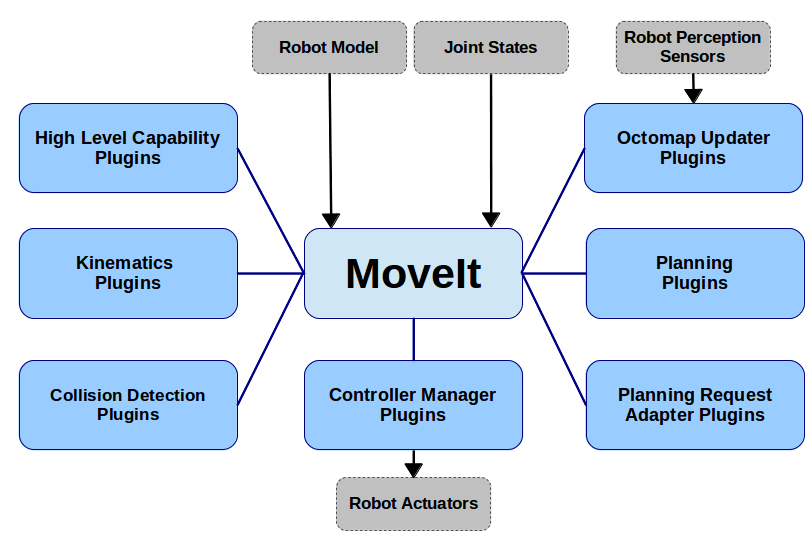
move_group::MoveGroupCapability
By implementing the move_group_capability.h interface it is possible to realize functionalities that are executed frequently. Each capability has access to the move group context including e.g. obstacle for collision avoidance.
Plugins of this type usually create communication functionality in form of a ros-action or a simple ros-topic and can operate on the move group context. Therefore, can be the possible applications very diverse.
The interface is defined in the move_group_capability.h. It mainly consists of an initialize function which has to be overwritten.
Moveit offers a number of default capabilities. A description of these can be found here.
An example for a specific plugin is the cartesian_path_service_capability. This particular plugin can be used to compute a cartesian path. The implementation of the initialized function is shown below. In the example the plugin advertises a topic containing information about the trajectory and a service for computing a new trajectory.
void move_group::MoveGroupCartesianPathService::initialize()
{
display_path_ = node_handle_.advertise<moveit_msgs::DisplayTrajectory>(planning_pipeline::PlanningPipeline::DISPLAY_PATH_TOPIC, 10, true);
cartesian_path_service_ = root_node_handle_.advertiseService(CARTESIAN_PATH_SERVICE_NAME, &MoveGroupCartesianPathService::computeService, this);
}
kinematics::KinematicsBase
The KinematicsBase interface enables you, to:
The well documented interface is located here.
Examples for implementations of the KinematicsBase are
planning_interface::PlannerManager
Base class for MoveIt planners. By implementing it you can hook your own planners up to MoveIt.
The interface is defined in planning_interface.h.
MoveIt’s default implementation of this interface is the OMPL Planner.
planning_request_adapter::PlanningRequestAdapter
The concept of this type of plugin is explained as part of the MoveIt concept documentation.
Update/adjust a motion planning request before it passed to the solver and manipulate the resulting motion plan as generated by the planner. By default the following adapters are used in MoveIt:
cup/handle) to an object or robot frame (e.g. cup)The interface is located here.
The planning request adapters are currently specified in ompl_planning_pipeline.launch generated for each robot. Examples for implementations of the PlanningRequestAdapters can all be found in this moveit_ros_planning folder
moveit_controller_manager::MoveItControllerManager
MoveIt does not enforce how controllers are implemented. To make your controllers usable by MoveIt, this interface needs to be implemented. The main purpose of this interface is to expose the set of known controllers and potentially to allow activating and deactivating them, if multiple controllers are available. It is often the case that multiple controllers could be used to execute a motion. Marking a controller as default makes MoveIt prefer this controller when multiple options are available. The manager also coordinates the switch between two controllers. A controller can be active or inactive. This means that MoveIt could activate the controller when needed, and de-activate controllers that overlap (control the same set of joints)
The interfaces are defined in controller_manager.h. A concrete implementation can be found here: moveit_simple_controller_manager
controller_manager.launch could be look like this:
<launch>
<rosparam file="$(find xamla_egomo_moveit_config_dev)/config/controllers.yaml"/>
<param name="use_controller_manager" value="true"/>
<param name="trajectory_execution/execution_duration_monitoring" value="true"/>
<param name="moveit_controller_manager" value="moveit_simple_controller_manager/MoveItSimpleControllerManager"/>
</launch>
where the controllers are defined in the ‘controllers.yaml’.
moveit_ros_control_interface::ControllerHandleAllocator
By implementing the ControllerHandle.h interface it is possible to offer allocations of handlers for action based controllers. The controller handler are based on the class MoveItControllerHandle. These handlers communicate with the controller in order to e.g. send trajectories.
TODO
The interface is defined in ControllerHandle.h.
An exemplary implementation of this interface is the joint_trajectory_controller_plugin.cpp. This is also currently the only implementation available.
moveit_sensor_manager::MoveItSensorManager
This plugin is used to integrate sensores into the planning process. Defined in: sensor_manager.h
Holds information of sensors e.g.: The maximum distance along the Z axis at which observations can be executed. It can point a sensor towards a particular point in space. This may require executing a trajectory, but it may or may not execute that trajectory. If it does not, it returns it as part of the sensor_trajectory. This is the recommended behaviour, since the caller of this function can perform checks on the safety of the trajectory. The function returns true on success (either completing execution successfully or computing a trajecotory successfully)
TODO
constraint_samplers::ConstraintSamplerAllocator
TODO
TODO
TODO
collision_detection::CollisionPlugin
Plugin API for loading a custom collision detection robot/world.
namespace my_collision_checker
{
class MyCollisionDetectorAllocator :
public collision_detection::CollisionDetectorAllocatorTemplate<MyCollisionWorld, MyCollisionRobot, MyCollisionDetectorAllocator>
{
public:
static const std::string NAME_;
};
const std::string MyCollisionDetectorAllocator::NAME_("my_checker");
}
namespace collision_detection
{
class MyCollisionDetectionLoader : public CollisionPlugin
{
public:
virtual bool initialize(const planning_scene::PlanningScenePtr& scene, bool exclusive) const
{
scene->setActiveCollisionDetector(my_collision_checker::MyCollisionDetectorAllocator::create(), exclusive);
return true;
}
};
If you want to use a customized collision detection algorithm for self-collisions or collisions with the environment then this is the plugin that provides the necessary interfaces.
The interface is defined in the collision_plugin.h. It mainly consists of an initialize function which has to be overwritten.
NO IMPLEMENTATIONS AVAILABLE
occupancy_map_monitor::OccupancyMapUpdater
TODO
TODO
TODO
TODO
planning_interface::Planner
Deprecated!
Old base class for MoveIt planners which has been removed in commit daa9fd2062df65e713e6c40570b2f7dceafed178. Was replaced by PlannerManager. This class can still be found in use by outdated code, for example SBPLMetaPlanner and ChompPlanner.